S5P3 Students will investigate the electricity, magnetism and their relationship.
b. Determine the necessary components for completing an electric circuit.
c. Investigate common materials to determine if they are insulators or conductors of electricity.
b. Determine the necessary components for completing an electric circuit.
c. Investigate common materials to determine if they are insulators or conductors of electricity.
Electrical Circuits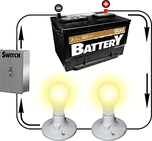
There are a few key components for any simple electrical circuit to work. You need a power source (battery or electrical generator), wire and a bulb or device. A switch is also handy, so you can easily turn the flow of electricity on and off. There can be no gaps in the circuit or electricity will not flow.
I would like to especially recommend the following resources: Start ExperimentingI have included a video about how to make a potato battery. After watching the video you should now be able to impress your friends, but why stop there? There are hundreds of electricity experiments that you can do. You now know the basics of electrical circuits. Start experimenting! Make sure that you ask permission before you begin an electrical experiment and NEVER USE AN ELECTRICAL OUTLET AS PART OF YOUR EXPERIMENT. You should use batteries for all electrical experiments. For step by step instructions of the potato battery, click here.
|
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are any objects that permit electricity to flow through them. The most common examples are any type of metal, such as copper, iron, steel, aluminum, silver and even gold. Water is also a good conductor of electricity, which is why you have to get out of the pool during a lighting storm. Insulators are materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them. Rubber and plastic are great insulators and that is why wiring that goes to your TV, computer and other electrical devices is encased in plastic.
If you are not sure if something is a conductor or an insulator, test it in a simple circuit. If the circuit still works than it is a conductor. If it does not work than it is an insulator. NEVER USE AN ELECTRICAL OUTLET AS PART OF YOUR EXPERIMENT. You should use batteries for all electrical experiments.
|
